EMAIL:
info@longhuamachine.com
TELL/whatsapp:
+8619305527239  English
English English
EnglishViews: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-09 Origin: Site








Aluminum die cast machines achieve high accuracy by combining advanced engineering, precise process control, and strict quality assurance. You benefit from aluminum die casting because it produces complex parts with excellent mechanical properties that meet strict tolerances. Manufacturers use rigorous quality control, including dimensional inspections and material testing, to verify each part. This precision ensures reliable performance and builds customer trust.
Aluminum die casting achieves high accuracy through advanced engineering and strict quality control, ensuring reliable performance.
Proper die design and material selection are crucial for minimizing defects and maintaining precision in aluminum die casting.
Regular calibration of die cast machines helps identify deviations, reducing defects and boosting productivity.
Real-time monitoring and automation enhance accuracy by allowing instant adjustments and early detection of potential issues.
A robust quality assurance program, including in-process inspections and final testing, ensures that every part meets strict industry standards.

Precision in aluminum die casting starts with the design and engineering of both the die and the machine. You rely on these elements to achieve consistent, high-quality results. Let’s break down how each factor contributes to accuracy.
You benefit from advanced die design because it directly affects the dimensional accuracy of aluminum die casting parts. Designers use simulation software to model the die casting process before production. This step helps predict shrinkage rates and optimize process parameters, reducing the risk of defects.
Simulation software, such as STAR-Cast, models how molten metal and air interact. This prevents trapped air and improves the integrity of each casting.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) addresses potential manufacturing challenges early.
Consistent wall thickness minimizes defects and ensures uniform cooling.
Ideal draft angles make it easier to remove parts from the die, which increases accuracy.
Precise tolerances guarantee that parts meet strict specifications.
Tip: Consistent wall thickness and proper draft angles help you avoid common casting defects.
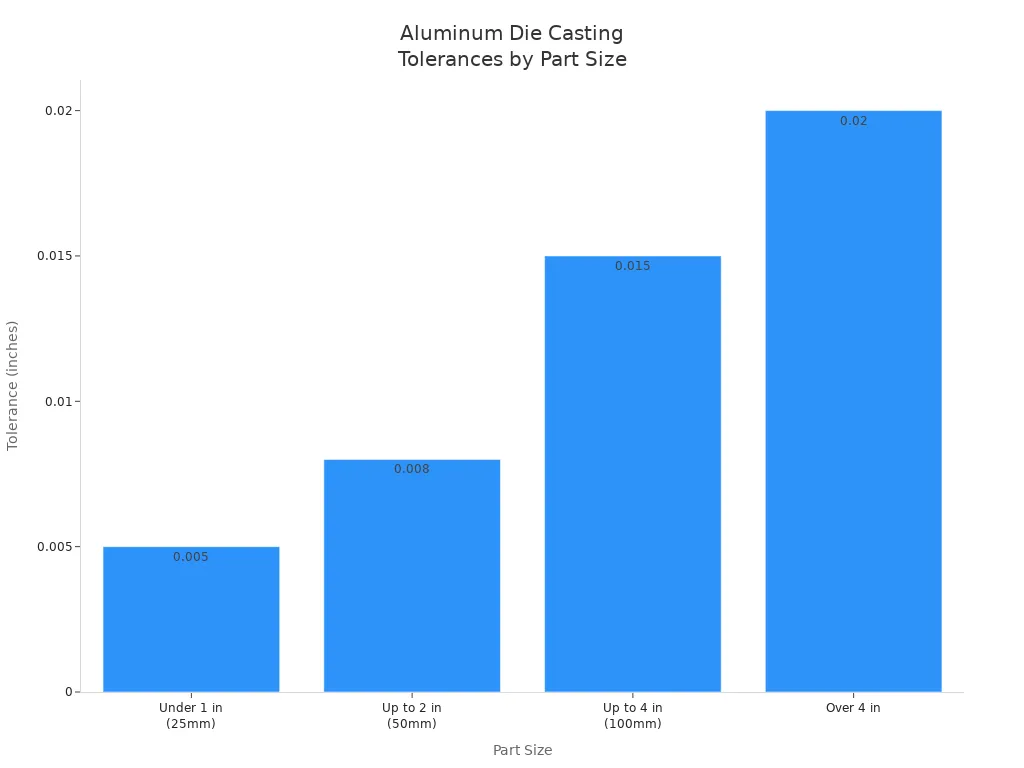
Here’s how industry-standard tolerances are classified for die and machine precision in aluminum die casting:
Grade A: Strictest tolerances for critical areas.
Grade B: Moderate tolerances for general applications.
Grade C: Lower accuracy requirements.
Part Size | Tolerance |
|---|---|
Under 1 in (25mm) | ±0.005 in (±0.13mm) |
Up to 2 in (50mm) | ±0.008 in (±0.20mm) |
Up to 4 in (100mm) | ±0.015 in (±0.38mm) |
Over 4 in | ±0.02 in (±0.51mm) |
General Standard | ±1% to 2% of nominal dimension |
Selecting the right materials for dies is essential for accuracy and durability in aluminum die casting. You want dies that last and maintain precision over many cycles. Most manufacturers choose tool steels and hot work tool steels because they offer high hardness and heat resistance. Nickel base alloys provide the longest die life, but they cost more and are harder to machine.
Material Type | Key Properties | Common Grades/Examples |
|---|---|---|
Tool Steels | High hardness, heat resistance, good machinability, cost-effective | A2, A6, D2, H13 |
Hot Work Tool Steels | Maintains strength and hardness at high temperatures | H11, H13, H19, H21 |
Nickel Base Alloys | Longest die life, high cost, machining difficulty | N/A |
Poor material selection leads to early mold failures. About 70% of early failures result from improper material choice or heat treatment. You can avoid costly downtime by understanding failure forms and choosing the right materials for your aluminum die casting dies.
Regular calibration of your aluminum die cast machine ensures it operates within specified tolerances. You need calibration to identify and correct deviations caused by wear and tear. This proactive approach minimizes defects and reduces scrap rates, which boosts productivity.
Calibration keeps temperature control systems functioning correctly.
Maintaining the ideal temperature range is essential for the die casting process.
Advanced machines provide superior control of injection pressure, speed, and temperature. These features help eliminate human error and ensure consistent quality.
CNC machining and automated measurement equipment verify that every casting meets required tolerances.
Digital inspection tools help you maintain high standards in aluminum die casting.
Note: Automotive aluminum die castings often require tolerances within ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm. Achieving these tolerances prevents misalignment and system failures.
You can rely on cold chamber die casting machines for aluminum alloys because they handle higher melting points and provide precise control. Machine engineering advancements, such as sensor connections and automated adjustments, further enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Precision in aluminum die casting depends on how well you control the process. You need to manage temperature, pressure, and machine selection to achieve consistent results. Each factor plays a unique role in minimizing defects and ensuring that aluminum die casting parts meet strict specifications.
You must pay close attention to temperature during the die casting process. The temperature of both the molten aluminum and the die itself affects the final product’s dimensional stability. Most aluminum alloys, such as A380, A360, and ADC1, require casting temperatures between 660°C and 710°C. You also need to keep mold temperatures between 180°C and 250°C. This careful control helps you produce complex shapes with consistent quality.
Proper temperature management controls how quickly the metal cools and solidifies. This step is critical for maintaining the mechanical properties and accuracy of aluminum die casting.
If you prevent rapid cooling in certain areas, you reduce gas entrapment. This leads to a denser and more uniform structure.
When you optimize temperature, you also minimize die maintenance needs. This boosts production efficiency and lowers costs.
Tip: Use flow front maps and solidification time maps to identify areas where uneven filling or cooling might cause stress or dimensional variation.
Simulation technologies, such as ProCAST and Mold Flow Analysis, help you visualize the flow path, temperature distribution, and solidification sequence. These tools allow you to adjust process parameters before production begins, reducing the risk of defects.
Pressure control is another key factor in aluminum die casting. You need to apply the right amount of pressure to fill the die completely and evenly. The optimal pressure range for aluminum die casting is between 100 and 1000 bar. During the second stage of injection, you should use pressures between 200 and 400 bar. This step removes air gaps and improves the structural integrity of the casting.
High pressure ensures that molten aluminum reaches every part of the die, even in thin or complex sections.
Consistent pressure reduces the chance of defects, such as porosity or incomplete filling.
You can use simulation technologies like CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) and FEA (Finite Element Analysis) to predict how pressure will affect the die casting process.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Simulation Technologies | Techniques like CFD, FEA, and thermal stress analysis predict metal filling and cooling behavior. |
Cooling System Optimization | Enhances cooling efficiency to reduce dimensional variations. |
Design for Manufacturability | Focuses on optimizing die design to minimize defects and variations during casting. |
Operator training also plays a big role. Skilled operators know how to set up machines, recognize defects, and maintain equipment. Their expertise helps you achieve high accuracy in every casting.
You need to choose the right machine for your application. Cold chamber die casting and hot chamber machines offer different benefits and levels of accuracy. Cold chamber die casting is the preferred method for aluminum alloys because it handles higher melting points and provides better control over the process.
Feature | Cold Chamber Die Casting | Hot Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
Dimensional Accuracy | High dimensional accuracy and consistency | Lower accuracy due to metal flow control |
Material Compatibility | Suitable for higher melting point alloys | Suitable for lower melting point alloys |
Cycle Time | Slower cycle time but versatile | Faster due to immediate availability of metal |
Cold chamber die casting is widely used in industries that demand high precision, such as automotive, medical, and aerospace.
Hot chamber machines work better for metals with lower melting points, but they do not provide the same level of accuracy for aluminum die casting.
Advancements in process control, such as Industry 4.0 technologies, have made it easier for you to monitor and adjust process variables in real time. At some manufacturing plants, AI systems collect thousands of data points for each shot. These systems analyze the data to identify conditions that lead to defects, allowing you to fine-tune the process and improve quality.
Note: By combining precise temperature and pressure management with the right machine choice, you can consistently produce high-quality aluminum die casting parts that meet demanding industry standards.
Automation and sensors play a key role in improving the accuracy of aluminum die casting. You can rely on these technologies to monitor, adjust, and detect errors during production. This approach helps you produce aluminum die casting parts with consistent quality.
You benefit from real-time monitoring systems that track process parameters every second. These systems use advanced algorithms and dashboards to visualize data and predict quality issues before they happen.
Monitoring System Type | Description |
|---|---|
Machine Learning Model | Uses data to predict quality and monitor process parameters, allowing early defect detection. |
Random Forest Algorithm | Predicts defects by analyzing mold temperature data, used in automotive engine component foundries. |
Data Visualization Dashboards | Shows prediction results to help you make better decisions in plant operations. |
Real-time data analytics, combined with AI and automation, reduces human error and increases dimensional accuracy. You see less material waste and more consistent results in aluminum die casting production lines.
Automation lets you adjust process variables instantly. You can control injection speeds, mold lubrication, pressure application, plunger speed, and pressure hold time. These adjustments ensure repeatability and accuracy in every cycle.
Parameter | Impact on Process |
|---|---|
Injection speeds | Ensures consistent filling of molds |
Mold lubrication | Reduces friction and mold wear |
Pressure application | Maintains uniform casting quality |
Plunger speed | Controls aluminum flow rate |
Pressure hold time | Affects solidification process |
Automated systems work well with cold chamber die casting. You get precise control over each step, which leads to better aluminum die casting results.
Tip: Automated adjustments help you maintain high standards and reduce downtime.
You need reliable error detection to catch defects early. AI visual inspection uses high-resolution cameras and smart algorithms to find cracks and surface flaws that manual checks might miss. This technology can scan thousands of parts per minute, making your quality control faster and more accurate.
X-ray inspection finds internal defects in aluminum die casting.
Skilled operators are needed, but automated systems make detection easier and more reliable.
Automated error detection is crucial for finding small defects and improving overall accuracy.
Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Deep learning-based detection (YOLOv5) | Achieves high precision (mean Average Precision of 0.971) for defect detection |
Real-time implementation | Detects and grades defects quickly without expensive hardware |
Applicability | Works for many metal parts that meet quality standards |
You can trust these technologies to keep your aluminum die casting process accurate and efficient.
Quality assurance stands at the core of producing accurate aluminum die casting components. You need a robust system to catch defects early and ensure every part meets strict standards. This process involves several steps, from in-process inspection to final testing.
You can use multiple inspection techniques during production to maintain accuracy in aluminum die casting. These methods help you spot issues before they become costly problems:
Visual inspection lets you check for surface defects like cracks or roughness.
Dimensional measurement uses precision tools to confirm that aluminum casting parts meet tight tolerances.
Mechanical property testing checks tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance.
Non-destructive testing, such as X-ray or ultrasonic methods, finds hidden internal flaws.
Tip: Early detection of defects during production reduces scrap rates and boosts overall quality.
After casting, you must refine aluminum casting parts to achieve the required accuracy and finish. Post-processing can remove up to 60% of defects, making your components more reliable and visually appealing. Industries like automotive and aerospace demand this level of precision.
Trimming and deburring remove excess material, such as flash and gates, that could affect quality.
Shearing and sawing help you reach tight tolerances and smooth finishes.
You ensure that each part meets industry standards by following these steps.
Before shipment, you need to verify the accuracy of every aluminum die casting product. Final testing methods include:
Testing Method | Description |
|---|---|
Dimensional Inspection | Confirms parts meet required measurements, often using coordinate measuring machines (CMM). |
X-Ray Inspection | Reveals internal defects like cracks or voids. |
Liquid Dye Penetrant Inspection (LPI) | Highlights small surface imperfections using special dyes and developers. |
A comprehensive quality assurance program reduces defects and improves consistency. You benefit from reliable aluminum die casting results, lower rejection rates, and greater customer satisfaction.
You achieve high accuracy in aluminum die casting by combining die and machine precision, process control, automation, and quality assurance. Each element supports the others, creating a reliable system for producing consistent parts.
Predictive models use real production data to show how these factors improve product quality.
Regression methods help you find the best manufacturing parameters for aluminum die casting.
Many people think accuracy depends only on the machine. In reality, you need a complete approach that includes design, monitoring, and testing.
You get high accuracy from aluminum die cast machines because they use advanced controls, precise dies, and real-time monitoring. These features help you achieve tight tolerances and consistent results, especially when you use high pressure die casting for complex parts.
Hot chamber die casting uses a machine where the metal stays in a heated chamber. This method works best for metals with low melting points. Aluminum die cast machines usually use cold chamber methods because aluminum melts at higher temperatures.
You cannot use hot chamber die casting for aluminum alloys. The process works for metals like zinc or magnesium. Aluminum needs a cold chamber die casting machine because it requires higher melting temperatures.
Real-time monitoring lets you track temperature, pressure, and other variables during production. You can spot problems early, adjust settings, and keep every aluminum die cast machine running at peak accuracy.
You find aluminum die cast machines in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. These sectors need precise, reliable parts that only advanced die casting methods can provide.