EMAIL:
info@longhuamachine.com
TELL/whatsapp:
+8619305527239  English
English English
EnglishViews: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-06 Origin: Site








You use a die cast machine by pushing melted metal into a steel mold very fast and with strong force. This makes exact parts in a short time. Hot-chamber machines can make one part in 4 seconds. Some low-pressure methods need up to fifteen minutes for each part.
Hot-chamber machines: about 15 cycles each minute (4 seconds for one part)
Low-pressure casting: up to fifteen minutes for one part
Die casting is a quick way to make metal parts. Melted metal gets pushed into a steel mold. This method makes exact shapes and smooth surfaces.
Hot chamber machines work fast. They make parts in about 4 seconds. Cold chamber machines are used for bigger and stronger parts. These parts use metals that melt at higher temperatures.
Getting the die ready is very important. Cooling the metal slowly is also important. These steps help make good castings with fewer mistakes.
Aluminum die casting is used a lot. It makes parts that are light and strong. This is good for cars and electronics.
Checking and fixing the die cast machine often is needed. This helps stop mistakes and keeps the quality of the products the same.
Die casting helps you make metal parts fast. You use a die cast machine to push melted metal into a steel mold. The mold shapes the metal into the part you want. Die casting is special because it makes tricky shapes and smooth surfaces quickly. People use die casting machines for car parts, electronics, and tools.
When you do die casting, you follow these steps:
Mould Creation: You design and build the steel mold.
Mould Preparation: You clean and coat the mold so metal flows and comes out easily.
Metal Injection: You melt the metal and push it into the mold with a die cast machine.
Cooling: You let the metal cool down and get hard inside the mold.
Casting Removal: You open the mold and take out the finished part.
Finishing Operations: You trim, polish, or treat the part if needed.
Die casting is faster than other ways to shape metal. You get exact parts with fewer mistakes. You can make shapes that are hard to get with forging or machining. Die casting machines work quickly and give you smooth finishes.
Tip: Die casting is great if you need lots of parts fast. You save time and money, especially when making many items.
Die casting has many good features that make it different from other casting methods. You get these benefits every time you use a die cast machine:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
High-speed injection | You push melted metal into molds very fast. |
High-pressure application | You use strong force to fill the mold all the way. |
High productivity | You make many parts in a short time. |
Dimensional accuracy | You get parts with exact sizes, so you do less extra work. |
Complex shapes | You make detailed and tricky designs easily. |
Embedding parts | You can put other pieces inside the casting while making it. |
Limitations | You have some limits with cost, size, and which metals you can use. |
Die casting lets you make thin parts that are still strong. You get smooth surfaces and strong parts. You also save money because you do not need much extra work after casting.
You can pick hot chamber or cold chamber die casting machines. There are also vacuum, gravity, high-pressure, and low-pressure die casting methods. Each one works best for different jobs and metals.
If you want light and strong parts, you often use an aluminum die casting machine. Aluminum die casting machines help you make thin and tough parts. You see aluminum die casting machines in places that need good strength and conductivity.
Die casting machines give you the same results every time. This makes them good for making lots of parts. You get smooth surfaces and exact sizes, so you do not need much work after casting.
When you choose a die cast machine, you need to know the main types. The two most common are hot chamber and cold chamber die casting machines. Each type works best for certain metals and part sizes. You get different results depending on which die casting machine you use.
Here is a quick comparison to help you see the differences:
Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
Process Overview | Injection system sits in molten metal. | Injection system stays outside molten metal. |
Materials Used | Best for low melting point alloys (zinc, tin, lead). | Best for high melting point alloys (aluminum, magnesium). |
Speed and Efficiency | Faster cycles, quick part production. | Slower cycles, handles more alloys. |
Applications | Small to medium parts. | Larger, more complex parts. |
You use a hot chamber die cast machine when you want to make small or medium parts quickly. The injection system sits right in the molten metal bath. This setup lets you make parts fast because the metal is always ready. You often use hot chamber die casting machines for zinc, tin, or lead parts.
Hot chamber die casting machines work best for:
Small to medium-sized parts
Jobs that need high accuracy and smooth surfaces
Projects where you want to make many parts quickly
Tip: If you need a lot of small parts, a hot chamber die cast machine saves you time and gives you great results.
You use a cold chamber die cast machine when you work with metals that melt at higher temperatures, like aluminum or magnesium. The injection system stays outside the molten metal. You pour the melted metal into the chamber for each shot. This method takes a bit longer, but it lets you use stronger metals.
Cold chamber die casting machines work best for:
Larger or more complex parts
Aluminum die casting machine and aluminium die casting machine jobs
Projects that need strong, lightweight parts
You get more choices with a cold chamber die casting machine. You can make big parts or parts with tricky shapes. If you want to use an aluminum die casting machine, you will pick a cold chamber type.
Note: Always match your die cast machine to the metal and part size you need. This choice helps you get the best quality and speed from your die casting machines.

The die casting process uses a die cast machine to turn molten metal into strong, precise parts. You follow a series of steps to make sure each casting meets your quality standards. Each step in the casting process affects the final quality of the finished casting. Here is how you move through the process, from start to finish.
You start by preparing the die, which is the steel mold that shapes your casting. You clean the die to remove any leftover material from the last cycle. You then spray a special lubricant onto the die surface. This lubricant helps the molten metal flow smoothly and keeps the casting from sticking to the die. Good die preparation is key for high quality and easy removal of the finished casting.
Tip: Always check the die for damage or wear before you begin. A clean, well-maintained die gives you better results and longer die life.
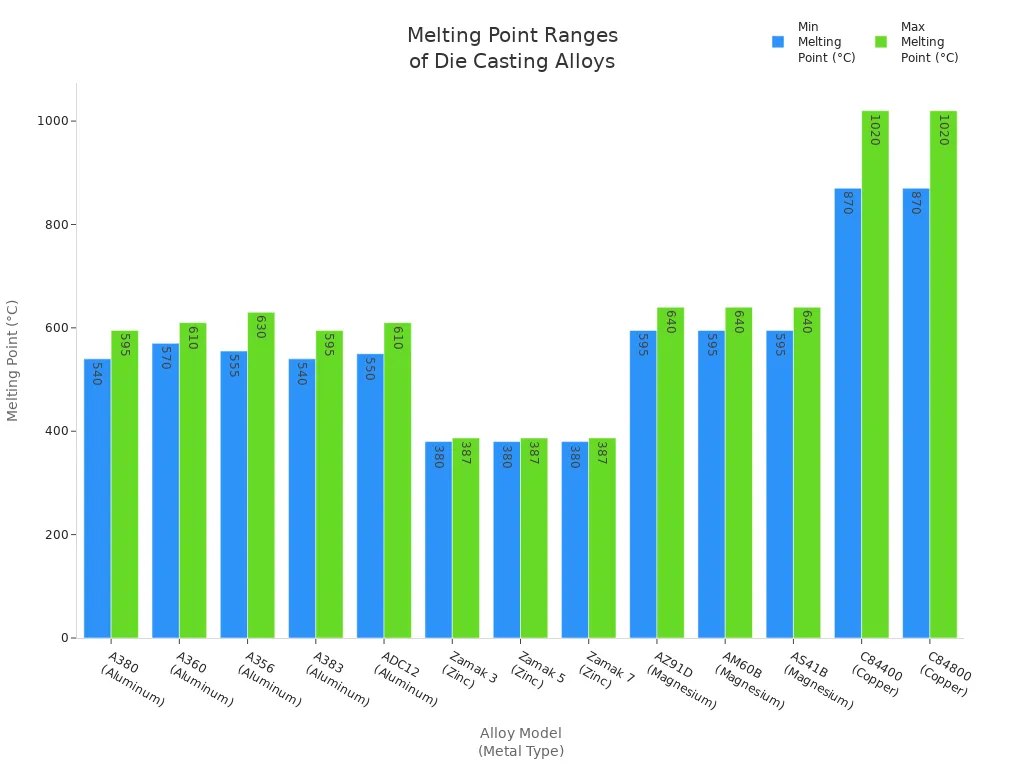
Next, you melt the metal you want to use for your casting. The temperature you need depends on the type of metal and alloy. For example, aluminum alloys like A380 melt between 540°C and 595°C (1004°F to 1103°F). Zinc alloys such as Zamak 3 melt at lower temperatures, around 380°C to 387°C (716°F to 728°F). Magnesium and copper alloys need even higher temperatures.
Here is a table showing common melting points for metals used in the casting process:
Metal | Alloy Model | Melting Point (°C) | Melting Point (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|
Aluminum | A380 | 540 - 595 | 1004 - 1103 |
A360 | 570 - 610 | 1058 - 1130 | |
A356 | 555 - 630 | 1031 - 1166 | |
A383 | 540 - 595 | 1004 - 1103 | |
ADC12 | 550 - 610 | 1022 - 1130 | |
Zinc | Zamak 3 | 380 - 387 | 716 - 728 |
Zamak 5 | 380 - 387 | 716 - 728 | |
Zamak 7 | 380 - 387 | 716 - 728 | |
Magnesium | AZ91D | 595 - 640 | 1103 - 1184 |
AM60B | 595 - 640 | 1103 - 1184 | |
AS41B | 595 - 640 | 1103 - 1184 | |
Copper | C84400 | 870 - 1020 | 1598 - 1868 |
C84800 | 870 - 1020 | 1598 - 1868 |
You use a furnace to heat the metal to the right temperature. The die cast machine keeps the metal at this temperature so it stays ready for the next step in the casting process.
Now you use the die cast machine to inject the molten metal into the die. This step is the heart of the casting process. The machine pushes the metal into the mold at very high speed and under high pressure. In high pressure die casting, the pressure can reach up to 140 MPa. This strong force fills every part of the die cavity, even the smallest details.
The high speed and pressure make sure the casting has a smooth surface and exact shape.
The process happens in just a few milliseconds, so the metal does not cool before it fills the die.
You can use traditional die casting, high vacuum die casting, or other methods, depending on the part and metal.
Note: High vacuum die casting removes air from the die before injection. This gives you better quality and fewer air bubbles in the casting.
After you inject the metal, you let it cool and harden inside the die. The cooling time depends on the thickness of the casting. For example:
A casting with a wall thickness of 3 mm solidifies in about 1.4 seconds.
A casting with a wall thickness of 11 mm takes about 6.1 seconds to solidify.
You keep the die closed during this stage to hold the shape and size of the casting. The die cast machine controls the cooling process to make sure the casting does not warp or crack. Good cooling gives you strong, high quality parts.
Once the casting has cooled and solidified, you need to remove it from the die. The die cast machine uses an ejection system to push the finished casting out of the mold. Here are the main mechanisms:
Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Ejector Pins | Pins that are driven by a moving ejector plate to push the casting off the die. |
Ejector Plate | A component that activates the ejector pins to facilitate the ejection of the cast part. |
Ejector System | The overall system responsible for ejecting the casting from the die cavity after solidification. |
You open the die, and the ejector pins push the casting out. You then check the finished casting for quality. If you use traditional die casting or high vacuum die casting, you may see small marks from the ejector pins, but these do not affect the quality of the part.
Tip: Always inspect the finished casting for cracks, warping, or surface defects. Good ejection helps you keep high quality in every casting.
Each step in the casting process, from die preparation to ejection, plays a big role in the quality of your finished casting. When you use a die cast machine the right way, you get strong, precise, and high quality parts every time.
You can pick from a few metals for die casting. The most used metals are aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and brass. Aluminum is the top choice for many jobs. Magnesium and zinc are good for parts with special needs. Magnesium is lighter than aluminum and keeps its shape well. Zinc gives a smooth finish and looks nice.
Aluminum is light and does not rust easily. This makes it great for die casting machine work. You use aluminum die casting for car parts, electronics, and tools. Magnesium is even lighter and helps make strong, thin parts. Zinc is best for shiny finishes and detailed shapes.
Aluminum die casting uses a die cast machine to push melted aluminum into a steel mold. You get parts that are strong, light, and exact. Many industries use aluminum die casting because it works fast and gives good results.
Here is a table that shows why aluminum is good for die casting:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Lightweight | Aluminum alloys weigh much less than steel. |
Mechanical Strength | Cast aluminum alloys make strong parts. |
Corrosion Resistance | Alloys like A360 form a layer that protects parts. |
Thermal Conductivity | Aluminum spreads heat well, good for engines and heat sinks. |
Aluminum die casting helps you make thin walls and tricky shapes. You use an aluminum die casting machine to make parts that are light and strong. The process gives smooth surfaces and exact sizes. You save time and money because you do not need much extra work.
Tip: Pick aluminum die casting if you want parts that are light, strong, and do not rust.
The metal you pick for your die cast machine changes the part you get. Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium each have their own strengths and looks. Aluminum die casting makes parts that are light and strong. Zinc die casting gives smooth finishes and lots of detail. Magnesium die casting makes the lightest parts.
Aluminum die casting is best when you want parts that last and do not weigh much. You see aluminum die casting in cars, bikes, and electronics. Choosing aluminum for your die casting machine means your parts will not rust and can handle heat.
Aluminum die casting also lets you make thin walls and hard shapes. You can count on aluminum die casting for strong, light, and tough parts. When you use an aluminum die casting machine, you get good results every time.
When the casting cools and gets hard, you take it out of the die. The die cast machine uses ejector pins and plates to push the part out. You should check the part right away for any problems. Some problems you might see are soldering, gas bubbles, heat cracks, blisters, flash, short fill, and cold shut. If you find any of these, you can fix them before the next step.
You do not want to damage the part when you take it out. Handle the part with care to keep its shape and surface nice. This step is very important for making good parts, especially for cars and other tough jobs.
Tip: Always look at each part after you take it out. Checking early helps you find problems before they go to the customer.
After you take out the casting, you need to finish it. These steps help you get the right look, feel, and strength for your part. Here is a table that shows the main finishing steps and why you use them:
Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Trimming | Cut off extra metal like flash, gates, and runners. | Get the part ready for assembly and make it look clean. |
Shot Blasting | Clean the surface with tiny rough pieces. | Make the surface smoother and get it ready for more work. |
Shot Peening | Hit the surface to make it stronger. | Help the part last longer by stopping cracks and breaks. |
Inspection and Quality Control | Use X-ray or sound tests to find hidden problems. | Make sure only good parts move on, so they are safe and work well. |
Dimensional Inspections | Check sizes with special tools. | Make sure the part fits right in other things, like car parts. |
Surface Finish Checks | Look at the surface to see if it is smooth and good. | Help stop rust and cut down on extra work later. |
You can also add special finishes to your die cast parts. Some common finishes are anodizing, powder coating, nickel plating, chrome plating, and Teflon coatings. These finishes help your parts fight rust, look better, and last longer. For example, anodizing gives a hard, colorful layer. Powder coating makes a tough surface that does not scratch easily. Many car companies use these finishes to protect and decorate their parts.
Other finishing steps like deburring and surface coating take off sharp edges and clean the part. Final finishes, like painting or plating, make the part stronger and look nicer. Good finishing gets your die cast machine parts ready for hard work in cars, electronics, and more.
Note: The right finishing steps help your parts last longer and look better. Pick the best way for your needs and where you will use the part.
You now understand how a die cast machine works from beginning to end. Here are the main steps you use with any die casting machine:
Put lubricant on the die.
Close and clamp the die halves.
Use the die cast machine to inject molten metal.
Let the metal cool inside the die.
Remove the finished part from the die.
Cut off any extra material.
Knowing each step helps you make strong and exact parts with your aluminum die casting machine or aluminium die casting machine. If you follow every step, you can find problems early and make better parts. For more help, look at the FAQ or check out these resources:
Resource | Description |
|---|---|
Die Casting 101 | Learn about die casting machines and best ways to use them. |
Shibaura Machine's Die Casting Training Programs | Get detailed training on how to use a die cast machine. |
You use both terms for the same equipment. A die cast machine or die casting machine pushes molten metal into a mold. Some people say "die cast machine" for the process, while "die casting machine" describes the equipment.
You can use an aluminum die casting machine for some metals, like magnesium. You should not use it for zinc or lead. Each die cast machine works best with certain metals. Always check the machine’s limits.
You clean the die cast machine after each use. You check for worn parts. You use the right lubricant. Regular checks help your die casting machine last longer and make better parts.
You pick an aluminium die casting machine because it makes light, strong parts. Car makers use these machines for engine blocks, wheels, and frames. Aluminum parts resist rust and help cars use less fuel.
You might see defects like cracks, bubbles, or rough surfaces. These problems come from wrong temperatures, dirty dies, or low pressure. You fix them by checking your die cast machine settings and keeping everything clean.