EMAIL:
info@longhuamachine.com
TELL/whatsapp:
+8619305527239  English
English English
EnglishViews: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-10 Origin: Site








A high pressure die casting machine lets you shape aluminum and magnesium into complex, accurate parts. You see high pressure force molten metal into detailed molds, filling every tiny feature. This speed and force give you parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances, often as precise as ±0.016mm. Consistent density and quality make these machines essential for modern manufacturing, especially when you need intricate designs.
High pressure die casting machines create precise, complex parts from aluminum and magnesium, ensuring smooth surfaces and tight tolerances.
The process involves several steps: mold preparation, metal injection, solidification, ejection, and finishing, each critical for quality production.
Aluminum and magnesium are preferred materials due to their lightweight, strength, and excellent castability, making them ideal for automotive, electronics, and aerospace applications.
High pressure die casting supports mass production, allowing manufacturers to produce thousands of identical parts quickly and efficiently.
Regular maintenance and careful process control are essential to avoid defects and ensure high-quality castings in large-scale production.

You use a high pressure die casting machine to create metal parts with precise shapes and smooth surfaces. High-pressure die casting works by melting metal, then forcing it into a steel mold at very high pressure. The process uses either cold chamber or hot chamber injection. Cold chamber injection requires pressures between 10,000 and 25,000 PSI, making it ideal for metals like aluminum. Hot chamber injection suits metals with lower melting points, such as magnesium.
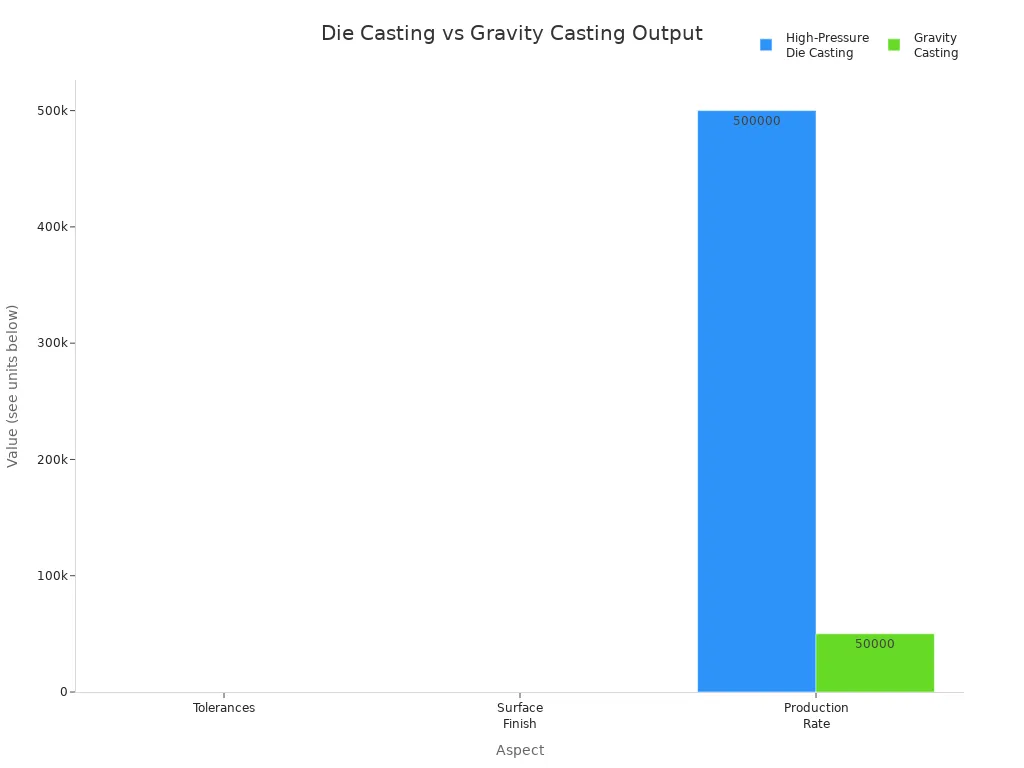
High-pressure die casting stands out because it produces complex parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. You can see the difference in the table below:
Aspect | High-Pressure Die Casting | Gravity Casting |
|---|---|---|
Injection Method | High pressure injection | Gravity fed |
Tolerances | +/-0.1 mm | +/-0.4 mm |
Surface Finish | 1.5 µm | 10 µm |
Production Rate | Up to 500,000 parts/year | Around 50,000 parts/year |
Tool Life | Lasts longer | Shorter lifespan |
Part Density | Denser parts | Less dense |
You inject molten metal into a locked die cavity, where it solidifies quickly under pressure. After solidification, you open the die and eject the finished casting. This method allows you to produce thousands of identical parts with high accuracy.
You often choose aluminum and magnesium for high-pressure casting because they offer unique advantages. Aluminum is lightweight, strong, and resists corrosion. It provides good dimensional stability and excellent castability, which means you can create intricate parts with thin walls. Aluminum alloys like A380 and ADC12 deliver high strength and thermal conductivity, making them perfect for demanding casting applications.
Magnesium stands out for its low weight and high strength-to-weight ratio. You can cast thinner walls and more complex shapes with magnesium alloys. Magnesium also offers better machinability and fine grain structure, which improves the quality of your finished parts. Both aluminum and magnesium allow you to achieve high productivity and precision in die casting.
Aluminum alloys: Preferred for high-temperature and long-lasting parts.
Magnesium alloys: Chosen for lightweight, strong, and precise castings.
You rely on high-pressure casting to produce parts for industries that demand accuracy, durability, and efficiency. The combination of high pressure die casting machine technology with aluminum and magnesium ensures you get the best results for your casting needs.
You start the high-pressure casting process by preparing the mold. This step is critical for producing quality parts. First, you clean the mold to remove any impurities that could affect the casting. You apply lubricants to the interior surfaces, which help regulate mold temperature and make it easier to extract the finished parts. Mold conditioning ensures the cavity is free from debris and ready for the next cycle.
Specialized coatings on the mold increase resistance to wear and corrosion. These coatings extend the lifespan of the mold and reduce production interruptions. For example, a high-grade PVD coating can boost mold life by up to 30%. You see fewer defects and more consistent parts when you use coated molds.
You also check the mold cavity for any damage or wear before starting the casting process. This inspection helps you avoid problems during high-pressure die casting.
Ordered List: Mold Preparation Steps
Clean the mold thoroughly.
Apply lubricants to the cavity surfaces.
Inspect the cavity for wear or damage.
Apply specialized coatings if needed.
Condition the mold to the correct temperature.
You move to the metal injection phase of the high-pressure die casting process. Here, you melt aluminum or magnesium and prepare to inject the molten metal into the mold cavity.
Cold chamber die casting requires you to ladle molten metal into a separate chamber. This method suits metals with higher melting points, such as aluminum and magnesium. Hot chamber die casting uses a built-in pool of molten metal and works best for lower melting point alloys.
You use a horizontal plunger to force the molten metal into the cavity at extremely high pressure. The typical pressure range for cold chamber die casting machines is 2,500 to 25,000 PSI. Some processes reach up to 31,000 PSI or use 400 to 4,000 tons of force.
High-pressure casting ensures the molten metal fills every detail of the cavity quickly. This rapid injection reduces the chance of defects and creates parts with tight tolerances.
You control the speed and pressure to optimize the metal casting process and prevent porosity. Precise control of injection parameters is essential for producing high-quality parts.
Unordered List: Metal Injection Highlights
Cold chamber die casting suits aluminum and magnesium.
Hot chamber die casting is faster but used for lower melting point alloys.
Injection pressures range from 2,500 to 31,000 PSI.
Horizontal plunger pushes molten metal into the cavity.
Rapid filling creates dense, accurate parts.
After injecting molten metal, you allow it to solidify inside the mold cavity. High-pressure casting speeds up solidification, which helps you produce parts quickly. The mold absorbs heat from the molten metal, causing it to harden and take the shape of the cavity.
You use several mechanisms to eject the solidified parts from the mold. Ejector pins push the parts out with controlled force, preventing deformation. Air ejection uses air pressure to reduce friction and avoid surface damage. Stripper plates slide or lift the parts off the core, minimizing distortion.
Mechanism | Description | Damage Prevention Features |
|---|---|---|
Ejector Pins | Forcefully push out the molded part without causing damage. | Controlled force (500-5,000 kg) to avoid deformation. |
Air Ejection | Utilizes air pressure to assist in ejecting the part from the mold. | Reduces friction and sticking, minimizing surface damage. |
Stripper Plates | Slides or lifts the part off the core after solidification. | Mechanical force ensures integrity and minimizes distortion. |
You inspect the parts after ejection to ensure they meet quality standards. You check for defects like porosity, cracks, or incomplete filling. Advanced techniques, such as vacuum-assisted die casting and optimized gating, help you reduce porosity and improve part quality.
You finish the high-pressure die casting process by treating the surface of the parts. Mechanical finishing includes grinding, polishing, deburring, and shot blasting. These steps remove excess material and improve the appearance of the parts.
Chemical finishing involves anodizing, chemical conversion coatings, and passivation. Anodizing increases surface hardness and adds a corrosion-resistant layer, which is important for automotive and aerospace applications.
Thermal finishing, such as heat treatment and tempering, enhances the mechanical properties of the parts. You may also apply coatings and paints, including powder coating, liquid painting, electrocoating, and electroplating.
Surface finishing improves both the appearance and performance of aluminum and magnesium parts. Techniques like painting and plating boost weather resistance and wear protection. Anodizing provides a durable, corrosion-resistant surface.
You use these finishing processes to meet specific requirements for color, texture, and durability. Surface treatments extend the service life of parts and ensure they perform reliably in harsh environments.
Unordered List: Common Finishing Techniques
Mechanical finishing: grinding, polishing, deburring, shot blasting
Chemical finishing: anodizing, chemical conversion, passivation
Thermal finishing: heat treatment, tempering
Coatings and paints: powder coating, liquid painting, electrocoating, electroplating
You complete the high-pressure casting process by performing final inspections. You use coordinate measuring machines, X-ray inspection, and pressure testing to verify the quality of the parts. These steps ensure that every part meets the required standards for strength, appearance, and reliability.
You gain many advantages when you use a high pressure die casting machine for aluminum and magnesium. This method supports large-scale production and delivers high-quality parts with impressive speed. You achieve short casting cycles, which means you can produce thousands of parts in a short time. The method ensures molten metal fills every detail of the mold, so you get precise shapes and tight tolerances. You see smooth surface finishes, which make your parts ready for electroplating or other treatments.
High-pressure casting lets you create complex shapes and thin-walled components that other methods cannot handle. You rely on this method for high volume production and consistent quality.
Here is a table showing the main benefits:
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Efficiency | Achieves short casting cycles, ideal for mass production of complex components. |
Precision | Ensures molten metal fills every detail, meeting strict appearance and dimensional tolerances. |
Surface Finish | Produces smooth surfaces, suitable for electroplating treatments. |
Complex Shapes | Capable of producing shapes that other methods struggle with. |
Thin-walled Components | Allows casting of thin-walled parts, unlike many other casting methods. |
You also benefit from high material utilization. High-pressure casting uses less raw material compared to forging, which helps you reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. You can optimize process parameters to lower greenhouse gas emissions and integrate waste heat recovery systems to minimize environmental impact.
You must consider some limitations when you use high-pressure die casting for aluminum and magnesium. This method requires careful control to maintain quality during large-scale production. You often face defects such as shrinkage porosity, gas porosity, and cold shuts. Early identification of these defects is crucial for high-quality parts.
Uneven cooling can cause warping or cracking, especially in complex mold designs.
You need regular maintenance because high-pressure casting leads to rapid tool wear.
Porosity may weaken parts if you do not vent the mold properly or if impurities enter the molten metal.
Natural shrinkage of aluminum during cooling can affect part dimensions, which is critical for high-precision applications.
Thermal fatigue may cause cracking or solidification defects, so you must design molds carefully to minimize thermal stresses.
You may also see exhaust gas produced during molten metal processing. You need to address resource consumption and waste generation by improving energy efficiency and integrating waste heat recovery systems. High-pressure casting demands constant attention to mold design, process control, and inspection to maintain quality and reliability in every part.
You see high pressure die casting machine technology play a major role in automotive production. Manufacturers use aluminum and magnesium to create lightweight, strong, and precise parts. You rely on high-pressure casting to produce engine blocks, transmission housings, and brake components. These parts must be durable and accurate to ensure vehicle safety and performance.
You also find die casting used for interior components such as seat frames, steering column supports, and instrument panel brackets. Structural and body components like subframes, suspension parts, and body panels benefit from the strength and low weight of aluminum and magnesium.
Engine blocks provide durability and reduce vehicle weight.
Transmission housings offer precision and reliability.
Brake components deliver strength and safety.
Chassis parts improve stability and crash protection.
High-pressure casting supports mass production, allowing you to manufacture thousands of identical parts quickly. You achieve tight tolerances and smooth finishes, which are essential for modern vehicles.
You depend on die casting to produce electronic housings and components. Aluminum and magnesium help you create lightweight, durable, and complex shapes for consumer electronics. High-pressure casting ensures uniformity and consistency, which protects delicate electronic parts.
You use aluminum for its durability and versatility. Magnesium allows you to design thin-walled and intricate parts.
High-pressure casting enables mass production of engineered metal parts with attractive finishes.
You see these materials used in laptop casings, smartphone frames, and camera bodies. The process supports high-volume production and meets the demands of modern electronics.
Application Area
Benefits
Automotive Components
Lightweight, complex shapes, high dimensional accuracy, and repeatability.
Consumer Electronics
Reduces weight and improves performance, critical for modern electronic devices.
High Volume Production
Suitable for mass production of engineered metal parts with attractive finishes.
Die casting allows you to meet strict requirements for shape, wall thickness, and tolerance in electronic device manufacturing.
You see high-pressure casting as a key process in aerospace production. Aluminum and magnesium parts weigh 15 to 25% less than those made by traditional methods. This weight reduction helps you lower fuel usage and emissions by up to 10%.
You use die casting to create complex geometries and precision parts for engine mounts, landing gear, and fuselage panels. Magnesium offers energy absorption and lightweight properties, which improve safety and payload capacity. Aluminum provides strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity for critical aerospace components.
Material | Key Performance Requirements | Applications in Aerospace |
|---|---|---|
Magnesium | Lightweight, energy absorption, high-temperature alloys | Seat risers, console brackets, clutch brackets |
Aluminum | Strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, versatility | Fuselage panels, wing structures, landing gear |
High-pressure casting lets you meet strict aerospace standards for reliability and performance. You produce parts that withstand extreme conditions and mechanical stress. |
You shape aluminum and magnesium with a high pressure die casting machine by following precise steps. You clean and preheat the die, melt the metal, and inject it at high speed and pressure. High-pressure casting fills every detail, giving you smooth, accurate parts. You trim and finish each casting for quality. High-pressure casting supports automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. You see new trends like digital simulation and recycled materials improving high-pressure casting. You can expect high-pressure casting to deliver even better results as technology advances.
High-pressure casting helps you create strong, lightweight parts that keep your business competitive.
You get precise, complex parts with smooth surfaces. High-pressure casting fills every detail of the mold quickly. This process supports mass production and delivers consistent quality for industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace.
You inspect molds before each cycle. You use lubricants and coatings to reduce wear. You check finished parts for defects using X-ray and pressure testing. Regular maintenance helps you avoid tool damage and ensures reliable production.
You can produce thin-walled parts with high-pressure die casting machines. The process uses strong force to fill molds completely. You achieve lightweight, strong components that meet strict dimensional requirements.
You use grinding, polishing, and shot blasting for mechanical finishing. Anodizing and chemical conversion add corrosion resistance. Heat treatment improves strength. These methods help you meet appearance and durability standards.
You select aluminum for its strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Magnesium offers low weight and high strength-to-weight ratio. Both metals allow you to create intricate, lightweight parts for demanding applications.